Fused filament fabrication
Fused filament fabrication is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. This is fed from a large coil, through a moving, heated printer extruder head. Molten material is forced out of the print head's nozzle and is deposited on the growing work piece. The head is moved, under computer control, to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in layers, moving in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane at a time, before moving slightly upwards to begin a new slice. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled, to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections.
Fused filament printing is now the most popular process (by number of machines) for hobbyist-grade 3D printing. As other techniques, such a photopolymerization and powder sintering, may offer better results at greater cost, they still dominate commercial printing.
Working Process
Flow geometry of the extruder, heating method and the melt flow behavior of a non-Newtonian fluid are of main consideration in the part.
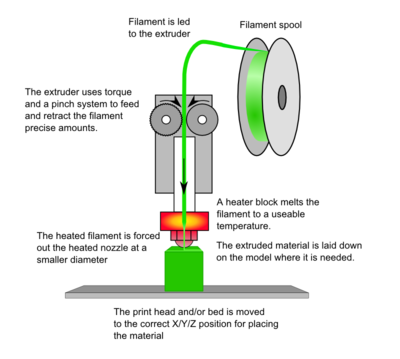
A plastic filament is supplied from a reel, either commercially available or homemade, and fed into a heated liquefier where it is melted. This melt is then extruded by a nozzle while the incoming filament, still in solid phase, acts as a ‘‘plunger.’’

The nozzle is mounted to a mechanical stage, which can be moved in the xy plane. As the nozzle is moved over the table in a prescribed geometry, it deposits a thin bead of extruded plastic, called a ‘‘road’’ which solidifies quickly upon contact with substrate and/or roads deposited earlier.
Solid layers are generated by following a rasterizing motion where the roads are deposited side by side within an enveloping domain boundary.
Once a layer is completed, the platform is lowered in the z direction in order to start the next layer. This process continues until the fabrication of the object is completed.
For Successful bonding of the roads in the process control of the thermal environment is necessary. Therefore, the system is kept inside a chamber, maintained at a temperature just below the melting point of the material being deposited.
Application areas
- Prototypesare produced for form / fit and functional testing in standard materials by FDM
- Support parts(jigs, fixtures, helps) can be produced directly
- Small series partsdown to one of a kind are built in standard materials by fused deposition modeling

